Search Results for: plant association
Plant association
plant association A grouping of plant species, or a plant community, that recurs across the landscape. Plant associations... Read More
Commensalism
Commensalism Definition What is commensalism? Literally, commensalism is a Latin word that means ‘to eat at the same... Read More
Plant Tissues
Plants are composed of three major organ groups: roots, stems, and leaves. As we know from other areas of biology, these... Read More
The consequences of antibiotic use in horticulture
Leading articlesFrederick R. Falkiner* Department of Clinical Microbiology, Trinity College, Dublin; Central Pathology... Read More
Null hypothesis
Null Hypothesis Definition Null hypothesis is defined as “the commonly accepted fact (such as the sky is blue) and... Read More
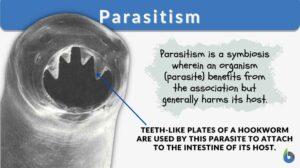
Parasitism
Organisms depend on different sources of food to survive. Larger organisms like plants make their own food (autotrophs) and... Read More
Mutualistic symbiosis
Mutualistic Symbiosis Definition In order to understand what a mutualistic symbiotic relationship means, we will break down... Read More
Macrophytes
Introduction Examples of Macrophytes. (Source: Canada's AquaticEnvironments) ... Read More
Seed Plants
There are two main subdivisions of seed plants—the ones without covered seeds, the gymnosperms, and the ones with covered... Read More
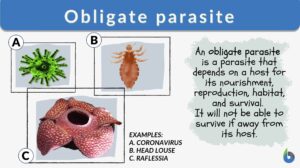
Obligate parasite
Parasitism is a form of symbiosis that occurs between a parasite and its host. The parasite is the organism that generally... Read More
Autocrine signaling
Autocrine Signaling Definition What is autocrine signaling? Autocrine signaling is a type of cell signaling wherein a cell... Read More
Nitrogen fixation
Definition noun The conversion of atmospheric nitrogen (N2) into a more usable form by natural means, such as by the... Read More
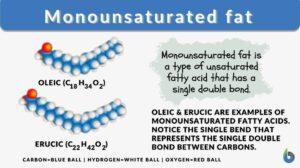
Monounsaturated fat
What is monounsaturated fat? Monounsaturated fats are healthy dietary fats. They are liquid at room temperature. Unlike... Read More
Triglyceride
Definition noun, plural: triglycerides An energy-rich compound made up of a single molecule of glycerol and three molecules... Read More
Genetic variability
Genetic Variability Definition Genetic variability refers to the tendency of individual genetic characteristics in a... Read More
Cell Structure
The interior of human cells is divided into the nucleus and the cytoplasm. The nucleus is a spherical or oval-shaped... Read More
Adaptation
Adaptation Definition In biology and ecology, adaptation refers to the process of adjusting behavior, physiology, or... Read More
Vascular Plants: Ferns and Relatives
These plants are seedless plants, but unlike the bryophytes, they do have vascular tissue (xylem and phloem). Because of the... Read More
Root nodules
Root nodule (Science: plant biology) globular structure formed on the roots of certain plants, notably legumes and alder, by... Read More
Community (biology)
Community, in biology, refers to the assemblage of interacting organisms (either of the same or different species)... Read More
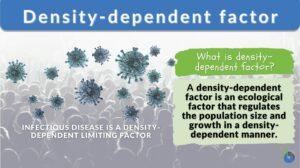
Density dependent factor
Density-dependent factors are the limiting factors of an ecosystem that regulate population growth in a density-dependent... Read More